Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy
Anyone with diabetes (Type 1, Type 2 & Gestational) can develop diabetic eye disease.
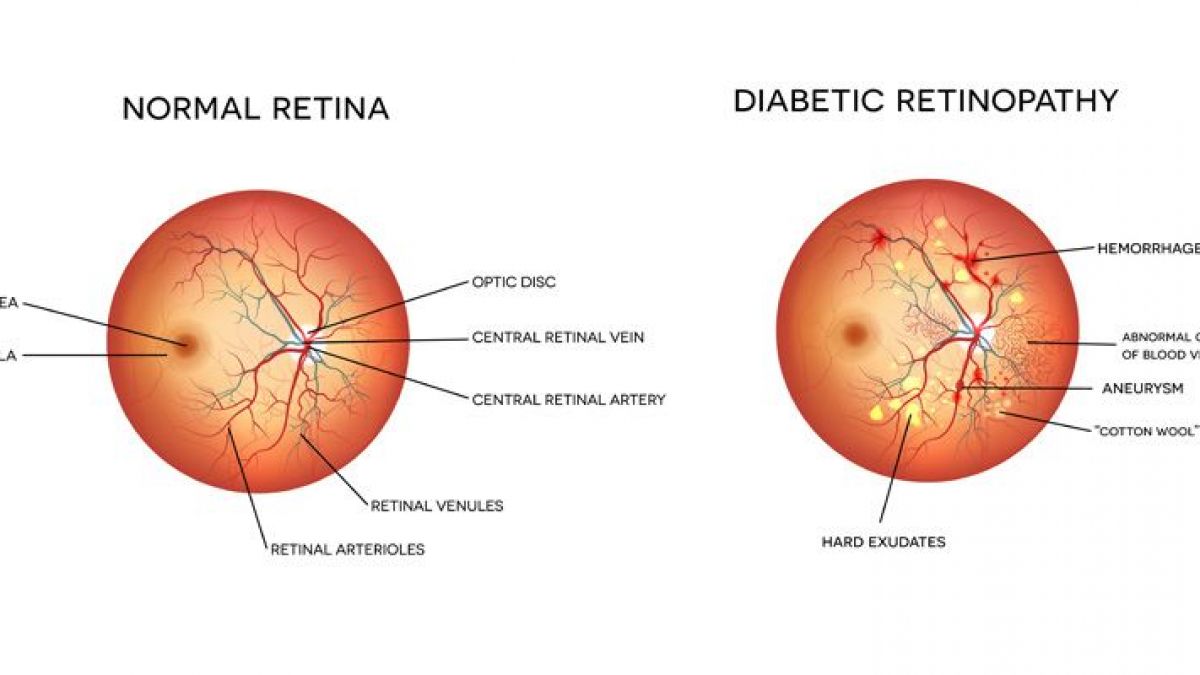
Diabetic retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes that affects the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels, causing them to leak or become blocked, which can lead to vision loss if left untreated. Your risk is even greater with:
- Untreated high blood glucose
- Untreated high blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Smoking
Diabetic Retinopathy
Anyone with diabetes (Type 1, Type 2 & Gestational) can develop diabetic eye disease.
Diabetic retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes that affects the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels, causing them to leak or become blocked, which can lead to vision loss if left untreated. Your risk is even greater with:
- Untreated high blood glucose
- Untreated high blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Smoking
In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy may not have any noticeable symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, you may experience:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Floaters (spots or strings that appear to float in your vision)
- Dark or empty areas in your vision
- Impaired color vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Vision loss
Vision with Diabetic Retinopathy

Normal Vision

Diabetic Retinopathy
Book an Appointment
It’s crucial to have regular eye exams if you have diabetes, especially if you’ve had it for a long time or have poor blood sugar control. Early detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy are essential to prevent vision loss. If you experience any changes in your vision, contact your eye doctor or schedule an appointment with an ophthalmologist who specializes in diabetic eye care.








